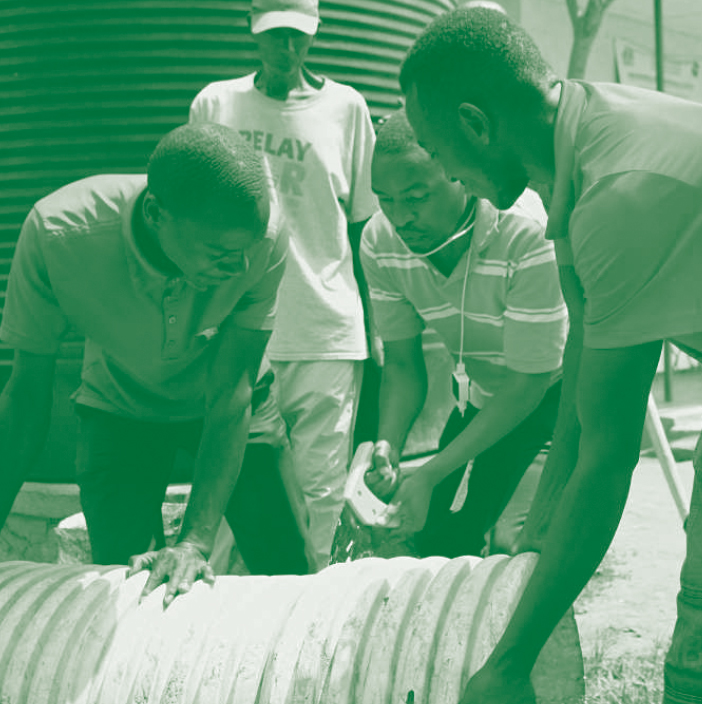
Diseño y sistemas hidropónicos Perspectivas desde y para el Norte y el Sur Global
Contenido principal del artículo
Resumen
Al enfrentar la complejidad del desafío que plantean el crecimiento urbano y el aumento de la población mundial, las disciplinas del diseño están llamadas a cuestionar nuevas estrategias para mitigar su impacto en la biodiversidad y el sistema de producción de alimentos. En este contexto, la hidroponía representa una solución viable para ayudar a restablecer una conexión con la naturaleza y crear vegetación productiva en los contextos más diversos. Aunque el potencial de estos sistemas se discute ampliamente desde diversas perspectivas, faltan estudios comparativos y evaluativos que ilustren su potencial para los diseñadores. A través del análisis de la literatura y los estudios de casos centrados en cultivos hidropónicos, pretendemos investigar las posibilidades y aspectos críticos que se ofrecen no solo para la producción de alimentos sino también como un medio para mejorar contextos degradados, desencadenar movimientos de innovación social y restaurar la identidad y los medios de vida de las personas y los territorios. Al comparar proyectos implementados en diferentes latitudes y la transferencia de soluciones de un contexto a otro, pretendemos dotar al Diseño de modelos virtuosos, integrando perspectivas del Norte y del Sur Global, para una mejor comprensión y nueva gestión de proyectos de estos sistemas.
Detalles del artículo
Citas
Balasubramanya, A. N., & Shaafiu, F. Z. (2022). Empowering Smallholder Farmers to Achieve Food Sovereignty Through Soil-Less Agriculture. [Master thesis, Uppsala University]. DiVA Portal. http://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:1694775/FULLTEXT01.pdf
Bason, C., Conway, R., Hill, D., & Mazzucato, M. (2020). A new Bauhaus for a Green Deal. UCL Institute for Innovation and Public Purpose. https://www.ucl.ac.uk/bartlett/public-purpose/publications/2021/jan/new-bauhaus-green-deal
Becattini, G. (2004). Industrial districts: A new approach to industrial change. Edward Elgar Publishing.
Boylan, C. (2020, November 9). The future of farming: Hydroponics. Princeton Student Climate Initiative. Retrieved June 24, 2023, from https://psci.princeton.edu/tips/2020/11/9/the-future-of-farming-hydroponics
Browning, W. D., Kallianpurkar, N. K., Ryan, C. O., & Labruto, L. (2015). The economics of Biophilia: why designing with nature in mind makes financial sense. Terrapin Bright Green LLC.
Castelló Ferrer, E., Rye, J., Brander, G., Savas, T., Chambers, D., England, H., & Harper, C. (2019). Personal Food Computer: A New Device for Controlled-Environment Agriculture. In: K. Arai, R. Bhatia, S. Kapoor (Eds.) Proceedings of the Future Technologies Conference (FTC) 2018. Vol 881 (pp. 1077-1096). Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-02683-7_79
Cifuentes- Torres, L., Mendoza- Espinosa, L. G., Correa-Reyes, G., & Daesslé, L. W. (2021). Hydroponics with wastewater: a review of trends and opportunities. Water and Environment Journal, 35(1), 166-180. https://doi.org/10.1111/wej.12617
Dholwani, S. J., Marwadi, S. G., Patel, V. P., & Desai, V. P. (2018). Introduction of Hydroponic system and it’s Methods. International Journal of Recent Technology Engineering, 3(3), 69-73. https://www.ijrti.org/papers/IJRTI1803011.pdf
Emmanuel, K., Sackey, A. S., & Awere, E. (2013). Assessment of the nutritional status of junior high school students-evidence from Mfantseman municipality of Ghana. Science Journal of Public Health, 1(5), 222-226. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.sjph.20130105.16
Fetting, C. (2020). The European Green Deal. ESDN Report, December 2020. ESDN Office. https://www.esdn.eu/fileadmin/ESDN_Reports/ESDN_Report_2_2020.pdf
Gallo, P. (2016). Tecnologia Idroponica per l’Agricoltura Urbana. Ingenio, 40, 1-11. https://www.ingenio-web.it/articoli/tecnologia-idroponica-per-l-agricoltura-urbana/
Garden to connect. (n.d.). https://www.gardentoconnect.eu/
Gashgari, R., Alharbi, K., Mughrbil, K., Jan, A., & Glolam, A. (2018, August). Comparison between growing plants in hydroponic system and soil based system. In Proceedings of the 4th World Congress on Mechanical, Chemical, and Material Engineering (Vol. 18, pp. 1-7). Madrid, Spain: ICMIE. https://doi.org/10.11159/icmie18.131
Goldstein, H. (2022, August 18). MIT Media Lab Scientist Used Syrian Refugees to Tout Food Computers That Didn’t Work. IEEE Spectrum. Retrieved May 27, 2022, from https://spectrum.ieee.org/mit-media-lab-scientist-used-syrian-refugees-to-tout-food-computers
Inglese, G., Lucibello, S., Rotondi, C. (2023a). Resilience envelopes: the “fourth environment” as a source of inspiration, a place for speculation and a territory for experimenting with new models of life. Springer.
Inglese, G., Mura, A. M., Bonaiuto, M., Alves, S., Villani, T. (2023b). Biophilic Design for remote studying environments: Analysis of case studies involving a collaboration between Ergonomics and Environmental Psychology. Cumulus Antwerp Conference 2023.
Jagtap, S. (2019). Key guidelines for designing integrated solutions to support development of marginalised societies. Journal of Cleaner Production, 219, 148-165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.01.340
Jensen, M. H. (1997). Hydroponics worldwide. In International Symposium on Growing Media and Hydroponics 481 (pp. 719-730).
Khan, F. A. (2018). A review on hydroponic greenhouse cultivation for sustainable agriculture. International Journal of Agriculture Environment and Food Sciences, 2(2), 59-66. https://doi.org/10.31015/jaefs.18010
Khan, S., Purohit, A., & Vadsaria, N. (2020). Hydroponics: Current and future state of the art in farming. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 44(10), 1515-1538. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2020.1860217
Khokhar, T. (22 Mar. 2017) Chart: Globally, 70% of Freshwater is Used for Agriculture. https://blogs.worldbank.org/opendata/chart-globally-70-freshwater-used-agriculture
Lund, H. H., Exner, M., Jensen, N. E., Leggieri, M., Outzen, M., Ravn-Haren, G., von Sehested, M., Væring, A., & Andersen, R. (2022).
GrowBot: An Educational Robotic System for Growing Food. Applied Sciences, 12(11), 5539. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12115539
Malorgio, F. (2004). Le colture fuori suolo per le produzioni floricole di serra. Quaderno Arsia, 5, 2004.
Manos, D. P., & Xydis, G. (2019). Hydroponics: are we moving towards that direction only because of the environment? A discussion on forecasting and a systems review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(13), 12662-12672. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04933-5
McDonald, R. I., Mansur, A. V., Ascensão, F., Colbert, M. L., Crossman, K., Elmqvist, T., ... & Ziter, C. (2020). Research gaps in knowledge of the impact of urban growth on biodiversity. Nature Sustainability, 3(1), 16-24.
Morelli, N. (2006) Industrialisation and Social Innovation: Design in a New Context, in Friedman, K., Love, T., Côrte-Real, E. and Rust, C. (eds.), Wonderground - DRS International Conference 2006, 1-4 November, Lisbon, Portugal. https://dl.designresearchsociety.org/drs-conference papers/drs2006/researchpapers/27
Mougeot, L. J. (2000). Urban agriculture: Definition, presence, potentials and risks, and policy challenges. Cities feeding people series; rept. 31.
Nagendra, H., Bai, X., Brondizio, E. S., & Lwasa, S. (2018). The urban south and the predicament of global sustainability. Nature sustainability, 1(7), 341-349.
New European Bauhaus start-up Nabo Farm:“Waste is built into our current food system.” (2022, November 14). EIT Food. Retrieved June 24, 2023, from https://www.eitfood.eu/blog/new-european-bauhaus-start-up-nabo-farm-waste-is-built-into-our-current-food-system
Paguaga, H. (2022, June 17). Desertification and drought: In El Salvador ‘green gold’ takes on the Dry Corridor. Innovation Accelerator - WFP. Retrieved June 24, 2023, from https://www.wfp.org/stories/el-salvador-el-nino-crops-farming-central-america-dry-corridor-un-hydroponics
Richa, A., Touil, S., Fizir, M., & Martinez, V. (2020). Recent advances and perspectives in the treatment of hydroponic wastewater: a review. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology, 19(4), 945-966.
Rigolon, A., Browning, M. H., Lee, K., & Shin, S. (2018). Access to urban green space in cities of the Global South: A systematic literature review. Urban science, 2(3), 67.
Ryan, C. O., Browning, W. D., Clancy, J. O., Andrews, S. L., & Kallianpurkar, N. B. (2014). Biophilic design patterns: emerging nature-based parameters for health and well-being in the built environment. ArchNet-IJAR: International Journal of Architectural Research, 8(2), 62.
Snyder, H. (2019). Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines. Journal of Business Research, 104, 333–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.07.039
Somerville, C., Cohen, M., Pantanella, E., Stankus, A., & Lovatelli, A. (2014). Small-scale aquaponic food production: integrated fish and plant farming. FAO Fisheries and aquaculture technical paper, (589), I.
Suartana, I. W., & Suryanawa, I. K. (2020). Application of Green Economy in Malini Agro Park. Journal of A Sustainable Global South, 4(2), 23.
Torraco, R. J. (2005). Writing integrative literature reviews: Guidelines and examples. Human Resource Development Review, 4, 356–367. https://doi.org/10.1177/ 1534484305278283.
Tsekleves, E., Darby, A., Ahorlu, C., Pickup, R., de Souza, D., and Boakye, D. (2020) Challenges and Opportunities in Conducting and Applying Design Research beyond Global North to the Global South, in Boess, S., Cheung, M. and Cain, R. (eds.), Synergy - DRS International Conference 2020, 11-14 August, Held online. https://doi.org/10.21606/drs.2020.145
Turner, W. R., Nakamura, T., & Dinetti, M. (2004). Global urbanization and the separation of humans from nature. Bioscience, 54(6), 585-590.
UN General Assembly, (2015) Transforming our world : the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Retrieved September 2, 2023 https://www.refworld.org/docid/57b6e3e44.html
United Nations World Food Programme (2019, November 7). How to grow food in the desert slums of Lima. Innovation Accelerator. Retrieved June 24, 2023, from https://innovation.wfp.org/project/h2grow-hydroponics/how-grow-food-desert-slums-lima
Van Os, E., Stanghellini, C. (2001). Diffusion and environmental aspects of soilless growing systems. Italus Hortus 8 (6), 9-15.
Wilson, E. O. (1984). Biophilia. Harvard university press.
Wolfs, E. L. (2015). Biophilic design and Bio-collaboration: Applications and implications in the field of Industrial Design. Archives of design research, 28(1), 71-89.
World Food Programme, (2023, August 23). H2grow. Growing food in impossible places. H2Grow | WFP Innovation. Retrieved September 1, 2023 https://innovation.wfp.org/project/h2grow-hydroponics
WFP Innovation Accelerator. (2021, December 23). H2Grow Model Hydroponics School Garden | WFP Zambia [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UYmBXUNG5eQ